What is Acid Rain| Causes and its Effects
What is Acid Rain: Causes, Effects, Solutions?
What is Acid Rain?
The acid rain is a form of precipitation which may be fog or snow in which excessive acid like sulphuric or nitric acids are
The rainwater with a PH of less than 5.5 is called acid rain.
It can be harmful to plants, aquatic animals and human beings.
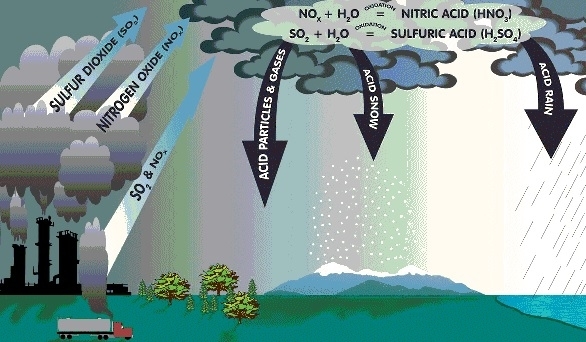
The two gases which are mainly responsible for causing acid rain are – Oxides of Sulphur (SO2) and Oxides of Nitrogen (NO2).
When SO2 and NO2 present in access amount in the atmosphere mixes or reacts with rainwater, they form sulphuric acid and nitric acid, respectively. These acids decrease the PH value of rain to less than 5.5 and make it acidic.
Causes of Acid Rain
The essential reasons for acid rain are as follows:-
Burning of fossil fuel
Exhaust from automobiles
Volcanic eruption
Sources of Acid Rain
(a) Sulphur
Natural sources:
Seas and oceans,
Volcanic eruptions,
Biological processes in the soil
Man-made sources:
Burning of coal
Petroleum products
Smelting of metal sulfide ores
Industrial production of Sulfuric acid
(b) Nitrogen
Natural sources:
Lightening,
Volcanic Eruption and
Biological Activity
Anthropogenic sources:
Forest fires
Combustion of oil, coal, and gas
(c) Formic Acid
(d) Other Acid
Effects of Acid Rain
Effects on plants – Acid rain erodes the waxy coating of plants damages the vegetation.
Effects on soil – Acid rain makes the soil acidic and infertile.
Effects on aquatic animals – Acid rain decreases the PH level of water bodies below 5.5 and makes them acidic. Results in the death of marine animals.
Effects on Monuments and Buildings – Acid rain reacts with the marble and other elements on the outer wall and makes them dull and yellowish (Ex - Tajmahal).
Surface and groundwater also get affected.
Solutions for Acid Rain
Reducing the burning of fossil fuels.
Use of eco-friendly measures in the automobile industry.
Plantation of trees.
Spreading awareness through various means.



Comments
Post a Comment
Useful